Diversifying forage composition to improve milk production and quality through participatory learning
07.05.2014
-
SUBMITTED ORGANISATION :
-
Integrated Organic Farming Systems Research Centre (IORC), Faculty of Agriculture, University of Brawijaya, Malang, Indonesia
-
DATE OF SUBMISSION :
-
07/05/2014
-
REGION :
-
South-Eastern Asia
-
COUNTRY :
-
Indonesia (Malang Regency)
-
SUMMARY :
-
Increasing economic and population growth in Indonesia has increased the demand for more protein. This growth has led to intensification of livestock production. Without good management, intensification might cause over grazing of natural resources in forest areas. Meanwhile, the widely practised management of supplying high yielding Elephant grass as the single type of fodder has not fulfilled livestock nutrient demands and has led to low milk production and quality. Taking into account land ownership and its conditions we introduced Crotalaria juncea, Lablab Purpureus (L) and Psophocarpus tetragonolobus L as complementary fodder types to be intercropped with other plants or grown as monoculture on the available land. The study was performed in Sumber Agung village of Ngantang sub-district in Malang using a participatory learning method that combined a field school and experimentation. The results show that Crotalaria is more robust than two other legumes due to its fast growing, ability to grow after some cuts and adaptability to be intercropped with other plants. Supplying Crotalaria to dairy cattle improved milk quality by 8-20% and milk productivity by5-8%. The improved quality and quantity of milk directly improved farmer’s revenue and livelihood.
-
KEYWORD :
-
forage, composition, livelihood
-
AUTHOR:
-
Adi Setiawan and Uma Khumairoh
Introduction
As the economy of Indonesia is growing along with the population, the need for protein from livestock products has increased. The higher demand for livestock products such as milk has encouraged farmers to intensify their farming systems by doubling their stocking rates and has even attracted new farmers. Since 2004, the population of dairy cows and milk production has been increasing. The largest increase of stock and milk production has occurred on East Java, followed by West Java and Central Java, respectively (Morelink Asia Pacific, 2011)
Similar to other developing countries, the majority of dairy farmers in Indonesia are smallholders with ownership of dairy cattle ranging from 1 to 20 heads and only 2 heads in average. Although the livestock sector is currently intensifying, it has not been accompanied with improved management of fodder production. Farmers still depend on natural sources of fodder and the availability of forage usually fluctuates from season to season. Farmers also utilize by- products and wasted crops to feed their livestock where it is not only less nutritious but also sometimes poisonous because of bacterial or fungal contamination (Byrne, 2007).
To face constraints of forage availability in intensive dairy farms, growing fodder crops is very important to support dairy farms operations. However, it can also become a dilemma because farmer landownership is very small, on average 0.5 hectare per farmer. On the one hand it is urgent to support dairy farm’s development by growing fodder; on the other hand, if the forage growing areas are expanded into the productive land for food, it will reduce food production of subsistence farmers. To reduce land use competition between feed and food growing purposes, a high yielding and nutritious fodders that are also tolerant to marginal land conditions need to be identified and developed.
Site description and the current situation of dairy farms
The participatory learning was performed in the village of Sumber Agung Vilage, Ngantang, Malang. Sumber Agung is located at7o52’50’’14S -112o23’13’’54T.With a total area of 756,688 ha, forest covers 40% of the area followed by agro-forestry (coffee and fruit trees) (36 % of the area) and rice field and arable farms (15% of the area). The remainder of the area is made up of housing, cemeteries and others use. As the area is bordered by 2 mountains, the village topography is hilly and slopy and the elevation is 800 m.a.s.l. Kalikonto is the main important river which has function as the main irrigation source and other livelihood. (Village Profile of Sumber Agung, 2012)
The majority of inhabitants are working in the agricultural sector both for dairy and plant production. The role of dairy cattle is to support smallholder daily life, to produce milk and also as a source of cash when needed. Since the availability of land to grow fodder is limited, many farmers utilize narrow or marginal land such as space under pine trees and road sides to grow fodder. Elephant grass became the dominant option for farmers to grow because of its high productivity. Responses of 20 farmers to our questions on the types of feed they use and its availability are given in Table 1.
Table 1. Farmer’s response to the types of feed and its availability
| No | Types | User | Availability |
| 1 | Elephant grass | 20 | 20 |
| 2 | Legume | 6 | 2 |
| 3 | Crop residues (maize&rice straw | 6 | 4 |
| 4 | By-products & others | 4 | 4 |
Table 1 shows that all respondents fed their livestock with elephant grass and only, 30% and 20% of the respondents diversify their forage composition with legumes, crop residues and by-products, respectively. 30% of the respondents, who supply their livestock with legumes and others (gliricidae and bush), explained that those fodders were collected from the areas near by the forest. However, their availability is fluctuating following a seasonal pattern. Whereas, residues are not only expensive when it is bought but it is also only available during harvest time.
Problems and potential solutions
The main problems found in the study site are the low quantity and quality of milk due to poor quality of feed. As forage in the study area, and in Indonesia as general, has been dominated by Elephant grass for energy, the proportion of protein fed to dairy cows is far lower than required. Further, the use of high amounts of concentrates is not economically feasible for small farmers. Hence, the quantity and the quality of milk in Indonesia is much lower than the genetic potential of the dairy cows. Farmers’ revenue is impacted by the low productivity and quality of milk.
To alleviate problems of poor quality fodder, complementing Elephant grass with a proportion a of legumes as protein sources could be an alternative. The main challenge then faced by small dairy farmers is to cultivate an appropriate composition of grasses and legumes, selecting legumes for better protein content and optimizing utilization of limited land to grow those legumes. High yielding, high protein content, palatability and quick recovery for cut and carry systems should be indicators. Additional options to cope with land shortage are to optimize space in between Elephant grass rows, use marginal lands, use the space under and between the trees or even to utilize fallowed rice field in between harvest and ploughing times to grow legumes.
Participatory learning processes
We started the learning processes by transecting the village and inviting farmer groups who might have common interest in the dairy farming systems. In the first meeting we set up the goal, identified the problems and potential solutions as well as the potential resources. In addition, to plan the learning processes, we selected topics to be learned about and set the meeting schedules including options for venues. Since all plans were prepared in a participatory way we expected that participants would feel responsible and commit to the all of the activities. The participatory decisions drawn from the first meeting are provided in Table 2.

During that first meeting we agreed to have meetings every two weeks to observe legume growth progression and to make plant measurements as a group as well. We used the trial as a learning medium. The first trial was aimed to find potential legumes to be grown as fodder and the second trial was aimed to understand the effect of legumes on milk quantity and quality. The trial set-ups are described below:
a. Legumes crop trial
In the first trial participants grew three kinds of legumes (Lablab Purpureus (L), Psophocarpus tetragonolobus L. and Crotalaria juncea (C) with 5 treatments: monoculture, intercropped with Elephant grass, intercropped under agro-forestry condition (fruit trees), intercropped with coffee, and intercropped with pine trees. The activities of seed selection and sowing are illustrated in Figure 1 and 2.
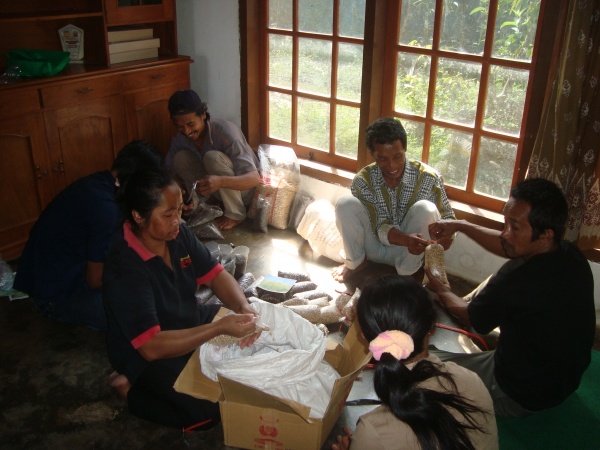


Figure 1. Participants prepare legume seed and sow it in monoculture treatment

Figure 2. Participants prepare legume seed and sow it in intercrop with Elephant grass and performance of L.purpureus (2nd picture)
After first harvest, legumes were fed to the cows. We interviewed participants to know their opinions on the feasibility of growing the three legumes and their utilization as fodder. Responses of 20 respondents to the questions are shown in Table 3.
Table 3. Farmer responses on three types of legumes as fodder
| No | Response on | L. purpureus | P. tetragonolobus | C. juncea |
| 1 | Easiness to grow | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| 2 | Easiness for maintenance | 7 | 5 | 16 |
| 3 | Easiness to harvest | 12 | 4 | 16 |
| 4 | Biomass production | 10 | 5 | 10 |
| 5 | Utilization (easiness to use) | 10 | 10 | 15 |
| 6 | Visually palatable for livestock | 12 | 12 | 16 |
Based on the interview, 100% of respondents said that it was easy to grow the three legumes. However, C.juncea had the highest score in terms of easiness to grow while P. Tetragonolobus and L. Purpureus were more difficult to manage. Opinions of the respondents did not differ greatly between L.purpureus and C.Juencea, however, in general C.junceawas more desirable. Thus, participants decided to continue the trial by only using C.juncea. The measurements executed by the participants on the potential of C.juncea to be grown both in monoculture and intercropped are provided in Table 4.
Table 4. Mean of biomass production of Clotalarian juncea in different cutting phases
| Treatments | 1st cut
(60 days after sowing) |
2nd cut
(30 after 1st cut) |
|
3.6 ton/ha | 3.2 ton/ha |
|
0.9 ton/ha | 0.5 ton/ha |
|
1.2 ton/ha | 0.9 ton/ha |
|
0.5 ton/ha | 0.1 ton/ha |
|
1.1 ton/ha | 0.8 ton/ha |
Table 3 shows the yield of C.juncea under different growing conditions. Although the highest yield was gained from monoculture, since C.juncea had less competition from the main plants, cultivating it as an intercrop offered greater potential to optimize land use.

Figure 3. Crotalaria performances
After establishing legumes in the first trial, participants continued for one month with the feeding trial. The trial was used to assess the effect of C.juncea on the quantity and quality of milk production. The feeding experiment was performed with8 cows. Four cows were in the 3 months lactation and 4 cows in the 4 months lactation. One cow from each period of lactation was treated as control and 2 other cows were fed C.juncea fodder. After being fed C.juncea for 15 days, daily milk production was measured as well as its grade (quality).The effect of C.juncea on milk quantity and quality are shown in Table 5.
Table 5. Effect of Crotalaria juncea on daily milk production per cow
| No. | Months of lactation | Cow I | Cow II | |||||
| Without C.juncea | With C.juncea | (%) increase | Without C.juncea | With C.juncea | (%) increase | |||
| 1 | 3 months | 16.97 | 17.88 | 5.1 | 15.06 | 16.52 | 8.8 | |
| 2 | 4 months | 17.52 | 17.88 | 1.9 | 18.42 | 18.38 | 0.5 | |
Table 5 shows that adding C.juncea to forage increased daily milk production. The highest increase was found in the cows at 3 lactation when they were fed with C.juncea, increasing by 5,1 % to 8,8% for cow 1 and cow 2, respectively. The effect of C.juncea on milk quality is shown in Table 6.
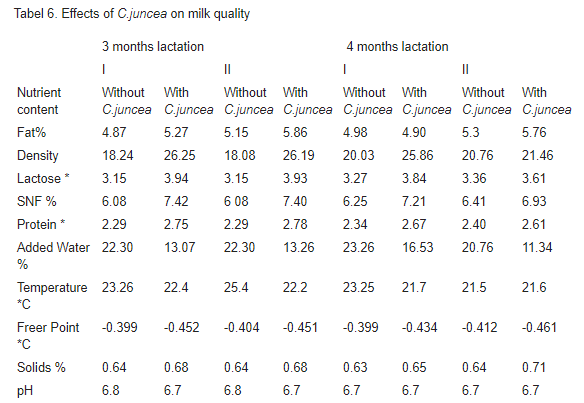
As with quantity, balancing feed composition using legumes increased the quality of milk in terms of protein. The higher increase was found in the cows with the lactation period at 3 months. Protein content of milk in which the 3 months lactation cows were treated with C.juncea increased by20-21% compared with the control. This increase occurred for the 4 months lactation as well, withan8-14% increase from the control.


Figure 5. Feeding trial with C.juncea
The better quality of milk increased the price of the milk from Rp.2800 toRp.3500 per litre. Together with the increase of milk production, farmers were able to increase their profits from milk production, leading to better incomes for their livelihoods.
Lessons learned
– The immediate results of these participatory learning activities were that farmers directly improved their revenue from the better performance of their dairy cows due to the transfer and sharing of knowledge through the participatory learning processes.
– Facilitators should understand the local situation including available social, economic and cultural resources. This local knowledge will equip facilitators to better organize and coordinate activities and to better engage with participants to build trust. This can be gained through survey and assessment before implementing the activities.
– The trust between facilitators and participants creates a positive atmosphere for the learning processes where participants openly accept and transfer their opinions. Thus a positive atmosphere contributes to the success of the activities.
– Materials, including both the manual and equipment should be well prepared. Facilitators should also be equipped with the basic knowledge of the topics and the local terms as well as communication skills and gaming. Those abilities make the activities more attractive to participants.
– Although the processes of participatory learning requires significant resources and logistical support, it can also be made cost and time effective by encouraging participants to be more committed and contribute to the activities. For example, if farmers provide experimental plots, the cost for renting field plots can be omitted.
– Female participation should be encouraged since their roles are also essential in the dairy farming activities. Greater female participation would make the impacts more visible.
– Exposing the activities to other stakeholders such as village staff, extension and cooperatives would provide more support and contribute to the long term sustainability of the activities.
– Since the participatory learning is follows the learning cycle concept, monitoring and evaluation is important. Monitoring and evaluation would help to gain better understanding of the systems, their pro’s and con’s and to plan the future actions.
– Well documented activities during the learning process would help the monitoring and evaluation processes.
Conclusion
Participatory learning is an effective approach to transfer and share knowledge between farmers and stakeholders. It is also a good way for stakeholders to establish networks and for communities to communicate. This may lead to the community problem solving. This is proved by the success of the trial performed by participants that engaged in the learning process. The participants experienced positive impacts including the better performance of their dairy cows due to balanced feed composition. The participating farmers gained better income to improve their livelihoods. A positive atmosphere created during this activity motivated farmers and stakeholders to participate and as a result the community became more open to accept and share knowledge.
Acknowledgment
We acknowledge the Nestle Corporation for their financial support for the success of our activities. Special thanks and gratitude to the dairy farmers who contributed their fields and cows as our learning medium as well as all participants.
References
Byrne Dan 2007. Dangers in feeding waste material to livestock. Prime Fact 311. New South Wales Department of Primary Industry. Australia. at: www.dpi.nsw.gov.au/primefacts
Indonesian Statistics. 2012. Village Profile of Sumber Agung, Sub-District of Ngantang in Malang District.
Morelink Asia Pacific. 2011. Indonesia Dairy Industry Development. Report to International Final Corporation. Australia. 59p. Available at http://www.ifc.org/wps/wcm/connect/93f48d00470e3bf883ffd7b2572104ea/Dairy+Industry+Development-2011.pdf?MOD=AJPERES
Pete Smith, P., Gregory, P.J., van Vuuren, D., Obersteiner, M., Havlík, P., Rounsevell, M., Woods, J.,Stehfest, E. And Bellarby, J. 2010. Competition for Land.Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B 27 September 2010 vol. 365 no. 1554 2941-2957. Doi.10.1098/rstb.2010.0127

